The opioid crisis represents one of the greatest public health challenges of our time, yet estimates of illicit opioid use are rare and typically available only years after data collection, limiting our ability to monitor trends in prevalence. This survey study estimated near real-time rates of illicit opioid use.
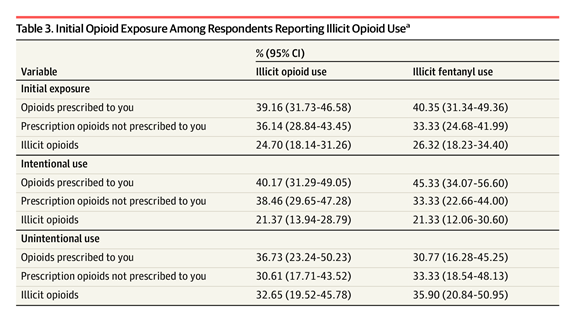
These findings suggest that illicit opioid use and, in particular, IMF use is more prevalent than previously estimated. Almost 11% of the population aged 18 years and older reported using illicit opioids within the past 12 months, including 7.5% of the population aged 18 years and older using IMF.
Research critical of prior survey evidence on illicit substance use estimated that the true rate of chronic heroin use was more than 16 times the rate reported in the NSDUH. Our estimate of IMF use is 25 times as large as the 2022 NSDUH rate for those aged 18 years or older (7.5% vs 0.3%). Assuming that illicit opioid use has increased, these differences are consistent with prior estimates of NSDUH undercounts of illicit opioid use.
Read more: JAMA Health Forum. 2025;6(5):e250809. doi:10.1001/jamahealthforum.2025.0809